EDUCATION
What Does ‘Disposed’ Mean in Court?

EDUCATION
University of Metaphysical Sciences Lawsuit: The Shocking Truth Behind Controversy

The University of Metaphysical Sciences lawsuit. This news brings up skepticism—Can a university dedicated to metaphysics really be taken seriously in a court of law? For others, it shines a spotlight on a bigger issue: the tension between mainstream accreditation systems and alternative, spiritual-based education.
You may be asking: What exactly happened, what’s the status of the lawsuit, and what does it mean for students pursuing metaphysical degrees? In this deep-dive article, we’ll unpack the facts, explore the context surrounding the University of Metaphysical Sciences in Sedona, Arizona, and provide the latest lawsuit updates for 2025.
Understanding the University of Metaphysical Sciences
The University of Metaphysical Sciences (UMS) is a private institution offering degrees in metaphysics, spirituality, meditation, holistic counseling, and consciousness studies. Its mission is clear: to provide comprehensive education in fields often overlooked by mainstream universities.
Located in Sedona, Arizona—a globally renowned hub for spiritual tourism, healing retreats, and “energy vortex” seekers—the institution fits seamlessly into the city’s identity. Sedona’s reputation for mystical exploration attracts students who resonate with spiritual growth and alternative learning.
Offerings include:
- Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral programs in metaphysical sciences.
- Online courses accessible worldwide, alongside in-person programs.
- Certification in holistic healing methods, spiritual counseling, and consciousness studies.
Clearly, UMS appeals to a specific audience—those more interested in spiritual evolution than traditional academic prestige.
What Sparked the University of Metaphysical Sciences Lawsuit?
The university of metaphysical sciences lawsuit revolves primarily around issues of accreditation, consumer protection, and transparency. Like many alternative or spiritual schools, UMS does not hold regional or national accreditation recognized by the U.S. Department of Education.
The lawsuit centered on claims that:
- Students were misled about the recognition and value of their degrees.
- Advertising language overstated credibility or career applicability.
- Compliance with state or federal regulations was unclear.
While UMS has long been open about its alternative status, the lawsuit reflects a recurring clash between regulators and schools outside conventional educational molds.
University of Metaphysical Sciences Sedona Arizona: Location and Symbolism
Why is the University of Metaphysical Sciences Sedona Arizona important to this discussion? It’s more than just a physical site—it’s a symbol. Sedona is famous for:
- Spiritual and metaphysical tourism.
- A thriving community of alternative healers, spiritual leaders, and holistic retreat centers.
- Global recognition as a spiritual hub.
For supporters, having a metaphysical university in Sedona legitimizes and strengthens the community. For skeptics, however, Sedona amplifies concerns that institutions there trade more on spiritual branding than academic rigor.
That dynamic is critical to how the lawsuit played out publicly.
Public Reactions: Mixed Voices
On social media and community forums, the lawsuit stirred intense debate.
One student praised UMS by writing, “I completed my metaphysical sciences degree online, and while I don’t use it for a corporate job, it guided me toward becoming a meditation teacher. That’s priceless.”
But critics counter with more practical concerns:
- Employers may not recognize these degrees.
- Students could invest significant money with limited professional payoff.
- Legal complaints suggest systemic problems with transparency.
The real challenge lies in balancing personal transformation (which many students report) with consumer protection and regulatory clarity.
University of Metaphysical Sciences Lawsuit Update (2025)
So, what’s happening now? The university of metaphysical sciences lawsuit update reveals progress in how UMS and regulators are addressing concerns.
- Clarification on Accreditation: The institution has updated marketing materials, explicitly differentiating itself from regionally or nationally accredited universities.
- Transparency Initiatives: UMS now provides clearer disclaimers about career prospects tied to metaphysical degrees.
- Settlement Discussions: Certain student complaints were resolved through private settlement. Details remain confidential, but reports suggest financial refunds were provided in select cases.
- Continued Operation: Importantly, UMS has not shut down. Programs continue, with renewed efforts to position the education as personal-development focused rather than career-preparatory.
The update demonstrates a critical point: alternative universities often survive lawsuits but emerge with adjusted policies around communication, compliance, and transparency.
The Bigger Picture: Why Alternative Education Faces Scrutiny
The case highlights larger systemic issues:
- Accreditation Bias – Mainstream academia often measures legitimacy solely by conventional accreditation.
- Consumer Protection – Students want reassurances about their financial investments in education.
- Philosophical Divide – Metaphysical sciences measure “success” in terms of personal enlightenment, not corporate job placements.
The tension isn’t about fraud vs. legitimacy—it’s about competing worldviews of what “real education” means.
Pros and Cons of Studying at UMS Amid Legal Controversy
Like any program, UMS comes with strengths and weaknesses.
Pros:
- Inclusive, global accessibility via online learning.
- Niche, specialized focus on metaphysics rarely found elsewhere.
- Deep community alignment with Sedona’s spiritual culture.
- Affordable compared to many traditional private universities.
Cons:
- Limited mainstream recognition of degrees.
- Difficulty in translating credentials into conventional employment.
- Legal challenges raise questions about long-term stability.
- Risk of mismatched expectations—students must know what they’re signing up for.
For some, the cons are deal-breakers. For others, the pros outweigh everything—particularly if personal spiritual growth is the main goal.
Lessons for Prospective Students
If you’re considering UMS or any similar institution, here’s what to remember:
- Research Thoroughly: Understand the accreditation status before enrolling.
- Define Your Goals: Are you after personal spiritual growth, or career advancement?
- Financial Clarity: Evaluate tuition relative to the value you personally expect.
- Seek Transparency: Ask for written clarification about degree recognition.
By doing this upfront, students avoid costly mismatches later.
FAQs About University of Metaphysical Sciences Lawsuit
1. What is the lawsuit against the University of Metaphysical Sciences about?
It concerned allegations of unclear degree recognition, consumer complaints about misleading claims, and compliance with educational regulations.
2. Is the University of Metaphysical Sciences accredited?
It is not accredited by U.S. Department of Education–recognized bodies. Instead, it operates as an alternative, private institution.
3. Can I get a job with a degree from UMS?
It depends. For traditional corporate or government jobs, recognition is limited. For holistic counseling, coaching, or spiritual careers, the degree may support credibility.
4. What’s the latest lawsuit update for 2025?
UMS has updated its marketing for transparency, resolved some complaints through settlements, and continues to operate while clarifying its educational mission.
Final Thoughts
The University of Metaphysical Sciences lawsuit isn’t just a courtroom drama—it’s a case study in how spiritual, nontraditional education collides with conventional standards. For supporters, UMS provides invaluable tools for personal transformation. For skeptics, it exposes the risks of vague promises and consumer misunderstanding.
In 2025, the updated lawsuit status shows the institution is adapting rather than disappearing. That’s an important reminder: alternative paths in education, though legally complicated, will always have a place in societies searching for meaning beyond conventional degrees.
EDUCATION
Reimagining Learning with Classroom 30X

Reimagining Learning with Classroom 30X
Integrating smart technology into education transforms traditional environments into dynamic, interactive learning hubs. Classroom 30X ushers in digital whiteboards, AI-powered analytics, blended learning strategies, and flexible seating to enhance student engagement and personalize instruction through adaptive tools and immersive content.
The Vision Behind Classroom 30X
Classroom 30X’s represents more than a tech upgrade—it’s a pedagogical shift toward student-centered learning spaces. This model blends physical infrastructure with learning management systems (LMS), interactive displays, and cloud-based analytics to create engaging environments. The traditional teacher-led model evolves into a facilitator-guided ecosystem that supports project-based learning, flipped classroom models, and collaborative problem-solving using digital tools like Google Workspace and PhET simulations.
Smart Displays & Interactive Whiteboards
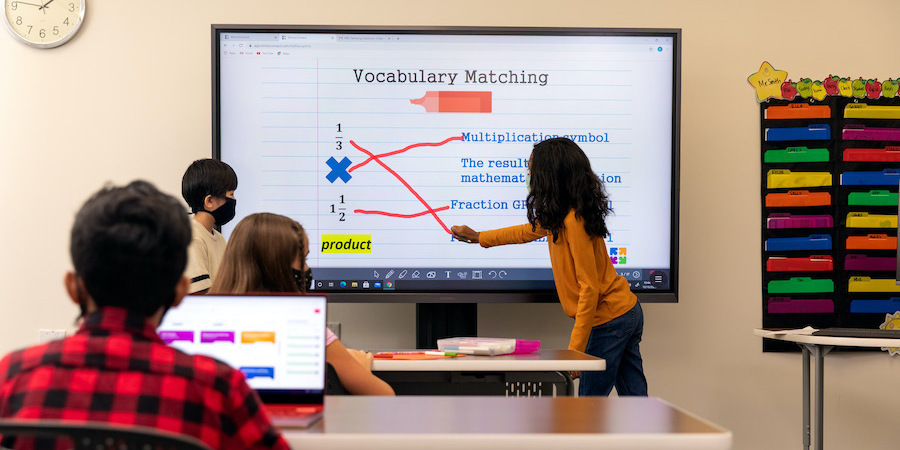
A hallmark of Classroom 30X is the installation of interactive whiteboards or smartboards that enable touch-based engagement on a large scale. Students can annotate lessons, manipulate multimedia, and collaborate in real time. Research suggests that interactive displays significantly boost participation and retention by fostering active learning .
These images illustrate modern touch-enabled classrooms with teachers guiding digitally interactive lessons.
Digital Infrastructure & Hybrid Connectivity
Effective implementation of Classroom 30X depends on robust digital infrastructure—high-speed Wi‑Fi, cloud storage, and learning analytics dashboards. This backbone supports synchronous lessons via video conferencing equipment like PTZ cameras and VoIP systems, integrating both in-person and remote learners in a blended learning environment .
Personalized & Adaptive Learning
With adaptive platforms built into Classroom 30X, students receive customized lessons based on performance data. Real-time analytics (via integrated LMS dashboards) help identify struggling learners and deliver tailored content, reflecting principles of mastery learning and adaptive assessment . For example, a math student can automatically be redirected to extra tutorials when their assessment shows gaps.
Gamification & Simulation Tools
Engagement is further boosted through gamified learning environments and interactive simulations like PhET. These tools encourage experimentation in virtual labs, enhancing critical thinking and retention. This aligns with Classroom 30X’s goal of fostering real-world problem-solving skills .
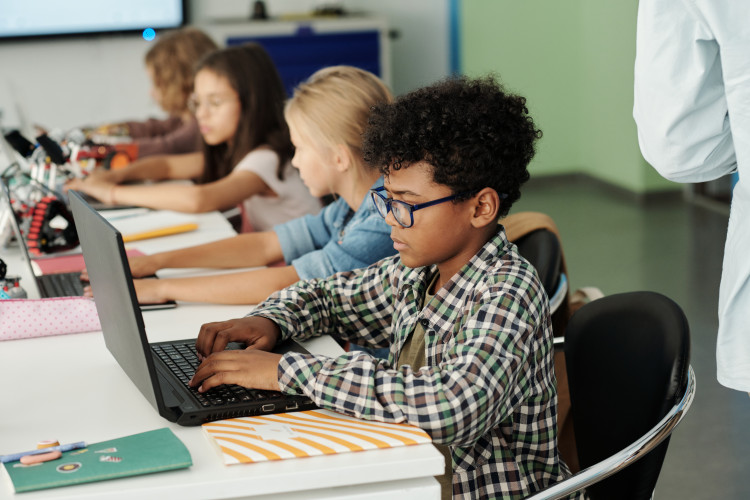
These images show students engaging with laptops and collaborative smart tables—key elements in tech‑forward classrooms.
Flexible Room Design & Seating
The physical layout of Classroom 30X promotes interaction. Modular desks, mobile whiteboards, and flexible seating configurations support group projects, peer-led discussions, and easy transition between instructional modes
Such adaptability encourages collaboration and efficient utilization of interactive tools.
Embedded Video: Examples in Action
Challenges & Considerations
Despite its benefits, Classroom 30X faces hurdles. The digital divide can hinder equitable access, particularly in low-resource districts
Teachers need thorough professional development to leverage these tools effectively. There’s also the risk of screen fatigue, making it critical to balance digital and offline activities . Finally, schools must establish robust data privacy and security policies to protect student information.
Future Trends: AI, AR, and Beyond
Looking ahead, Classroom 30X is poised to incorporate AI tutors, augmented reality (AR), and immersive holographic setups. Innovations like HoloBoards promise richer engagement and interactive lectures Edge computing and behavior recognition tools are also emerging, supporting advanced adaptive learning and teacher feedback systems .
FAQs
Q: What exactly does “30X” mean in Classroom 30X?
A: It refers to scaling up engagement and learning impact across a class of 30 students through integrated technology, pedagogy, and analytics .
Q: How does Classroom 30X support remote learners?
A: Powered by hybrid learning setups—like PTZ cameras and video conferencing—it enables seamless participation for both in‑person and online students.
Q: Do schools need advanced budgets to implement it?
A: Not necessarily. Schools can phase in tools, starting with mid-range smartboards and open‑source LMS, while building digital capacity over time .
Q: What role do teachers play in Classroom 30X?
A: Teachers transition into facilitators, guiding inquiry-based learning, interpreting analytics, and fostering student collaboration.
Q: Does AR/AI play a role in Classroom 30X?
A: Yes—future implementations include AR for immersive study and AI that adapts curriculum and assists with assessment.
Conclusion
Classroom 30X reimagines learning by blending interactive displays, adaptive analytics, flexible design, and gamified tools to foster a future-ready, student‑centered classroom. By balancing technology with pedagogical integrity, addressing equity, and prioritizing teacher development, it promises not just enhanced performance but a vibrant, engaging educational experience.
EDUCATION
Mastering Anatomy: Effective Study Tips for Exam Success
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoPure Clarity: The Power of Saline Contact Solution
-

 GENERAL10 months ago
GENERAL10 months agoUnveiling the 322 Messianic Prophecies: A Deep Dive
-

 TECHNOLOGY10 months ago
TECHNOLOGY10 months agoWhat happened to spank bang
-

 FASHION10 months ago
FASHION10 months agoDebonair blog:The Art of Stylish Living
-
 ENTERTAINMENT10 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT10 months agoWhat Is JerkMate? Exploring the Features and Purpose
-

 FASHION10 months ago
FASHION10 months agoUnderstanding the Carmelita Neck: A Unique Fashion Detail
-

 ENTERTAINMENT10 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT10 months agoDrake Exposed: The Untold Truth Behind the Music and Fame
-

 BUSINESS10 months ago
BUSINESS10 months agoCrypto FintechZoom: Navigating the Future of Digital Finance