EDUCATION
Mitochondria Role in Rainforest Ecosystems
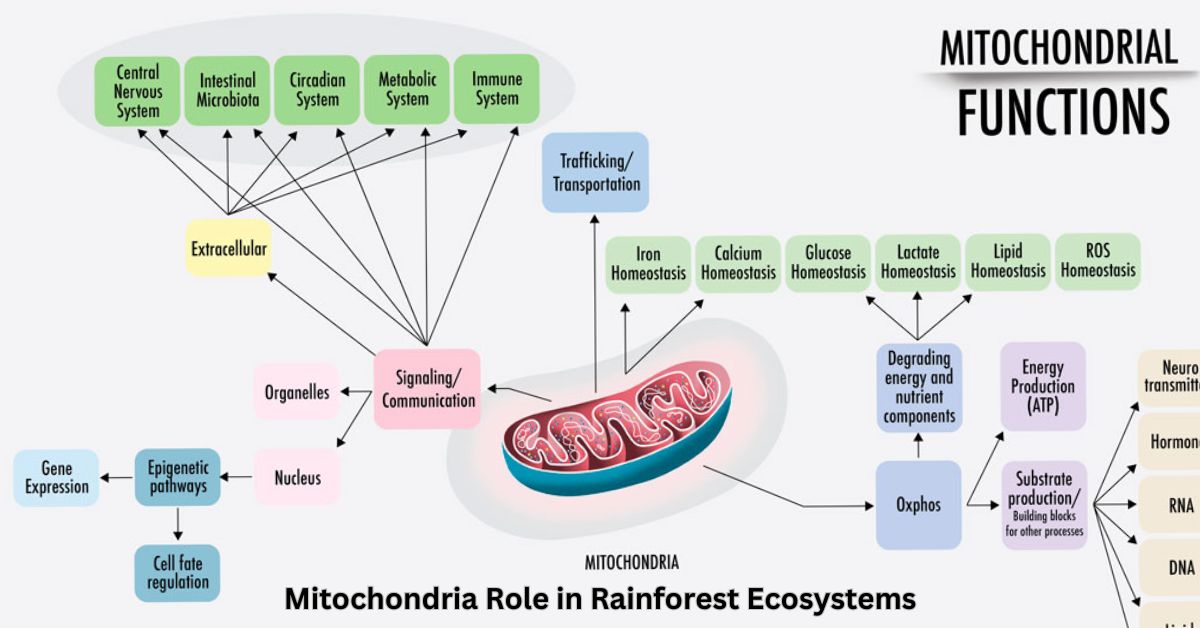
Mitochondria Role in Rainforest Ecosystems: A Powerful Link Between Life and Energy
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses” of cells, are crucial components of cellular biology. Their primary role is to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), fueling nearly every process that occurs within a living organism. But what does this cellular function have to do with something as vast and intricate as a rainforest ecosystem? At first glance, mitochondria and rainforests may seem worlds apart, yet a deeper look reveals how they are linked in surprising ways.
This article explores the fascinating connections between mitochondria and rainforest ecosystems, highlighting the roles of energy production, biodiversity, and sustainability in these vital natural habitats. Understanding this relationship helps us appreciate not only the function of mitochondria but also the importance of protecting rainforests, which play a significant role in sustaining life on Earth.
The Function of Mitochondria: Powering Life at the Cellular Level
Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. These microscopic structures are responsible for generating ATP through cellular respiration, a process that converts nutrients like glucose into usable energy. Mitochondria also have their own DNA, which allows them to replicate and adapt to the needs of the cell.
There are two types of respiration that occur in mitochondria: aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and produces the most energy, while anaerobic respiration can still generate ATP without oxygen, though less efficiently. This ability to produce energy is critical for the survival of nearly all living organisms, from single-celled bacteria to complex organisms like humans.
The energy produced by mitochondria supports countless biological processes, including growth, reproduction, and the regulation of homeostasis. In animals and plants, the ability to generate energy is fundamental to life, making mitochondria essential for survival. This central role in energy production connects mitochondria to the larger systems in which they exist, such as ecosystems like rainforests.
Rainforests: Complex Ecosystems of Energy and Biodiversity
Rainforests are among the most diverse and productive ecosystems on the planet. They are home to more than half of the world’s species, including countless plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. These ecosystems are critical to the global climate, acting as carbon sinks that absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide, helping to regulate the Earth’s atmosphere.
In a rainforest, energy flows through the system in a complex web of interactions. At the base of this web are primary producers, primarily plants, which use sunlight to produce energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then passed through the food chain, from herbivores to carnivores, creating a dynamic and interconnected system.
Much like mitochondria within a cell, the rainforest relies on a steady flow of energy to sustain its various processes. Without energy, life in the rainforest would cease, and the delicate balance of the ecosystem would collapse. But what does the production of energy in mitochondria have to do with the functioning of a rainforest? The connection lies in the shared reliance on energy to fuel processes, both at the cellular level and across entire ecosystems.
The Energy Connection: Mitochondria and the Rainforest
At first glance, mitochondria and rainforests may seem unrelated, but they share a critical link: both are involved in energy production, which is essential for the survival of living organisms. The energy produced by mitochondria in animals and plants supports individual organisms, while the energy flow in a rainforest ecosystem sustains the entire habitat.
-
Energy Flow in Ecosystems: Mitochondria play a role in the energy dynamics of an organism, converting nutrients into usable energy to fuel bodily functions. In a rainforest ecosystem, the energy produced by primary producers (plants) through photosynthesis supports herbivores, which in turn sustain carnivores. This flow of energy mirrors the function of mitochondria within a cell, where energy is passed through different levels, enabling organisms to grow, reproduce, and maintain homeostasis.
-
Biodiversity and Adaptation: Just as mitochondria can adapt to the needs of a cell, species in the rainforest evolve and adapt to their environment, allowing them to thrive in diverse niches. The energy produced by mitochondria supports these adaptations, whether it’s a predator’s need for energy to hunt or a plant’s ability to convert sunlight into energy for growth. In the same way, the rainforest’s biodiversity is maintained by the energy flowing through the ecosystem, which supports a wide range of species with different energy needs.
-
Interdependence of Organisms: The interdependence between different species in a rainforest ecosystem mirrors the way mitochondria work within a cell. Just as mitochondria rely on other organelles and cellular components to function optimally, species in the rainforest depend on each other for energy transfer. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil, which plants use for growth. This cycle of energy transfer ensures the sustainability of the ecosystem, just as mitochondria ensure the sustainability of life within a cell.
Mitochondria and the Carbon Cycle: A Critical Role in Climate Regulation
Mitochondria are not only essential for energy production within cells but also play an indirect role in regulating the broader environment. In both plants and animals, the energy produced by mitochondria is used to power metabolic processes that release carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Plants in the rainforest, through photosynthesis, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose, which provides energy for growth. However, when plants and animals respire, they release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
This process forms part of the carbon cycle, a natural process that regulates the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Healthy rainforest ecosystems act as carbon sinks, absorbing more carbon dioxide than they release. This helps mitigate the effects of climate change, as excess carbon dioxide is one of the leading contributors to global warming.
Mitochondria play a direct role in this process by regulating the energy production within organisms that contribute to the carbon cycle. The efficiency with which mitochondria generate energy affects the amount of carbon dioxide released through cellular respiration. In a way, mitochondria contribute to the overall health of the rainforest ecosystem by influencing how energy is processed and how carbon is cycled through the system.
Protecting Rainforests: The Impact of Mitochondrial Health on Ecosystems
Rainforests are under threat from deforestation, climate change, and other human activities. The loss of rainforests not only diminishes biodiversity but also disrupts the delicate energy flow that sustains these ecosystems. As mitochondria are crucial for energy production within cells, the health of rainforests is essential for maintaining the global energy balance that sustains life on Earth.
By protecting rainforests, we help maintain the intricate web of energy flow that sustains biodiversity and regulates the planet’s climate. Just as a malfunction in mitochondrial function can disrupt cellular processes, the destruction of rainforests disrupts the balance of energy production and consumption at the global level.
Conclusion: The Power of Energy in Life and Ecosystems
Mitochondria and rainforests may seem unrelated at first, but both share a crucial role in the production and flow of energy. Mitochondria provide the energy necessary for cellular function, while rainforests provide the energy that sustains diverse ecosystems. Together, these two systems highlight the fundamental importance of energy in sustaining life on Earth.
By understanding the links between mitochondria and rainforests, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate connections that exist in nature. Both at the cellular level and in the broader context of ecosystems, energy is the key to survival. Protecting rainforests is not just about preserving biodiversity; it’s about preserving the energy systems that support life on our planet.
In conclusion, the next time you think about mitochondria, remember that they are not just tiny powerhouses within our cells. They are part of a larger, interconnected world where energy flows from the smallest organisms to the largest ecosystems, including the majestic rainforests that cover much of our planet. Through these systems, life persists, adapts, and thrives.
EDUCATION
Mastering Anatomy: Effective Study Tips for Exam Success
EDUCATION
What Time Does Shabbat End? Understanding the Exact Moment

What Time Does Shabbat End? Understanding the Exact Moment
What time does shabbat end? Shabbat is one of the most significant and cherished observances in Judaism, offering a time of rest, reflection, and connection with family, friends, and God. It begins at sunset on Friday evening and lasts until the appearance of three stars in the sky on Saturday night. However, for those who observe Shabbat, determining the exact moment it ends can be a bit complex. In this article, we will dive into how to determine the time Shabbat ends, the significance of this moment, and what to consider when marking the conclusion of this holy day.
What is Shabbat?
Shabbat is the Jewish day of rest, commanded in the Torah (the Jewish Bible), where the Jewish people cease from their work and engage in spiritual practices, meals, prayers, and spending time with loved ones. It is observed from Friday evening until Saturday night, during which time Jews refrain from engaging in various forms of labor, in line with the commandment to “remember the Sabbath day and keep it holy” (Exodus 20:8).
The beginning of Shabbat is clearly defined as sunset on Friday evening, and it is concluded when three stars become visible in the night sky on Saturday. This marks the transition from the sacred day of Shabbat back to the ordinary weekdays.
When Does Shabbat End?
The end of Shabbat is traditionally determined by the appearance of three stars in the sky, signaling the nightfall. While this sounds simple, determining the exact time can vary based on location, time of year, and interpretation of Jewish law.
The Three-Star Rule
The “three stars rule” refers to the appearance of three medium-sized stars in the sky, which are considered visible when the sun has sufficiently set below the horizon. Once these stars are visible, the time of Shabbat’s conclusion is reached, and Jewish law allows for the resumption of regular weekday activities.
The reason why three stars mark the end of Shabbat is rooted in Jewish tradition and Talmudic law. The Talmud (Shabbat 34b) discusses how this is the general sign of nightfall. It’s important to note that this is not a specific hour, and the time varies depending on the season, geography, and local weather conditions. This is why many Jews rely on published times for the end of Shabbat in their area.
Time Variation Based on Location
Since Shabbat ends based on when three stars are visible, the exact time varies based on location. For example, in places closer to the equator, where the sun sets more quickly, Shabbat might end slightly earlier. In contrast, places further north or south may experience longer twilight periods, leading to a later time for Shabbat’s conclusion.
The Jewish calendar takes these variations into account by providing local times for candle lighting on Friday and the end of Shabbat on Saturday. The time difference can be as little as 30 minutes or as much as an hour or more, depending on where one is in the world.
Factors Affecting Shabbat’s Conclusion
Several factors affect when Shabbat officially ends. These include:
1. Geographical Location
- The time zone and geographical location determine how quickly the sun sets and when stars are visible in the sky. Jews living in different parts of the world will experience different sunset times and, by extension, different times for the conclusion of Shabbat.
2. Time of Year
- The time of year plays a significant role, as the earth’s tilt causes varying lengths of twilight in different seasons. For example, during the summer months, there is a longer twilight, meaning it takes longer for three stars to appear. In the winter months, the twilight period is much shorter.
3. Halachic Interpretations
- Jewish law, or Halacha, provides guidelines for determining the end of Shabbat. However, there is some debate within different Jewish communities regarding the specific time. Some interpret nightfall to occur a bit later than others, particularly when taking into account the varying levels of twilight in different locations.
4. Tzeit HaKochavim (Emergence of Stars)
- The exact time that three stars appear is known as “Tzeit HaKochavim,” and this can differ slightly depending on how clear the sky is, and the horizon’s visibility. In urban areas with high light pollution, it may be harder to see stars, requiring some to follow an estimated time published by local authorities.
How Do You Determine the Exact Time Shabbat Ends?
1. Using Jewish Calendars or Apps
The easiest way to determine the exact time Shabbat ends is by referring to a Jewish calendar, which provides accurate information for your area. These calendars list the times for candle lighting on Friday night and the end of Shabbat on Saturday night. Many Jewish websites and apps, such as “MyZmanim” and “Chabad.org,” allow you to enter your location and provide you with the specific time for Shabbat’s end.
2. Zmanim (Halachic Times)
Zmanim refers to the times according to Jewish law. For example, one common practice is to end Shabbat approximately 72 minutes after sunset, allowing for the three stars to appear. This 72-minute window is known as “Tosefet Shabbat” and ensures that there is ample time after sunset for nightfall to occur.
3. Following Local Synagogue Times
Many synagogues will also provide information about when Shabbat ends in their local community. These times are often based on the Zmanim for the area, providing a reliable way for members to know when they can resume activities after Shabbat.
4. Consulting a Local Rabbi
In communities without access to digital resources, consulting a rabbi or knowledgeable community member is a great option. They can provide precise, locally informed times for the conclusion of Shabbat.
What to Do After Shabbat Ends
The conclusion of Shabbat is marked by the Havdalah ceremony, which involves reciting prayers over a cup of wine, smelling spices, and lighting a special braided candle. This marks the distinction between the sanctity of Shabbat and the ordinary days of the week. After the Havdalah, people traditionally resume their work and other weekday activities.
The Significance of Shabbat’s End
While Shabbat is a day of rest and spiritual enrichment, its conclusion is also a time for reflection. The transition from Shabbat back to the regular workweek can serve as an opportunity for Jews to carry forward the peace and holiness of Shabbat into their daily lives. The end of Shabbat serves as a reminder that both the rest and labor in life should be balanced.
Why Is the Exact Time Important?
For many observant Jews, the exact moment Shabbat ends is crucial for several reasons:
-
Halachic Adherence: The observance of Jewish law requires precision in determining when Shabbat concludes. Violating this timing can result in the resumption of activities before the sacred day has ended.
-
Family and Community Practices: The end of Shabbat is often a communal time, where people gather for Havdalah or have family dinners. Knowing when to start this transition ensures that everyone can participate in this ritual.
-
Respecting the Holiness of Shabbat: By waiting until the proper time for Shabbat to end, Jews show respect for the sanctity of the day, ensuring that they fully observe all of its laws and rituals.
Conclusion
Determining the exact time that Shabbat ends can be complex due to various factors such as geographical location, time of year, and Halachic interpretations. However, by using resources such as Jewish calendars, apps, and local synagogue times, one can easily find the precise moment to conclude Shabbat. Whether you follow the traditional three-star rule or rely on local guidelines, understanding when Shabbat ends ensures that you honor this holy day correctly, marking the transition back into the regular week with respect and spiritual intention.
EDUCATION
What is the Date Two Weeks from Today?
-

 TECHNOLOGY3 months ago
TECHNOLOGY3 months agoWhat happened to spank bang
-
 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Is JerkMate? Exploring the Features and Purpose
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoUnderstanding the Carmelita Neck: A Unique Fashion Detail
-

 GENERAL3 months ago
GENERAL3 months agoUnveiling the 322 Messianic Prophecies: A Deep Dive
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoDebonair blog:The Art of Stylish Living
-

 BUSNIESS3 months ago
BUSNIESS3 months agoCrypto FintechZoom: Navigating the Future of Digital Finance
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoDrake Exposed: The Untold Truth Behind the Music and Fame
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Does It Mean to Be a Scratch Golfer?