GENERAL
What crops do apple snails eat
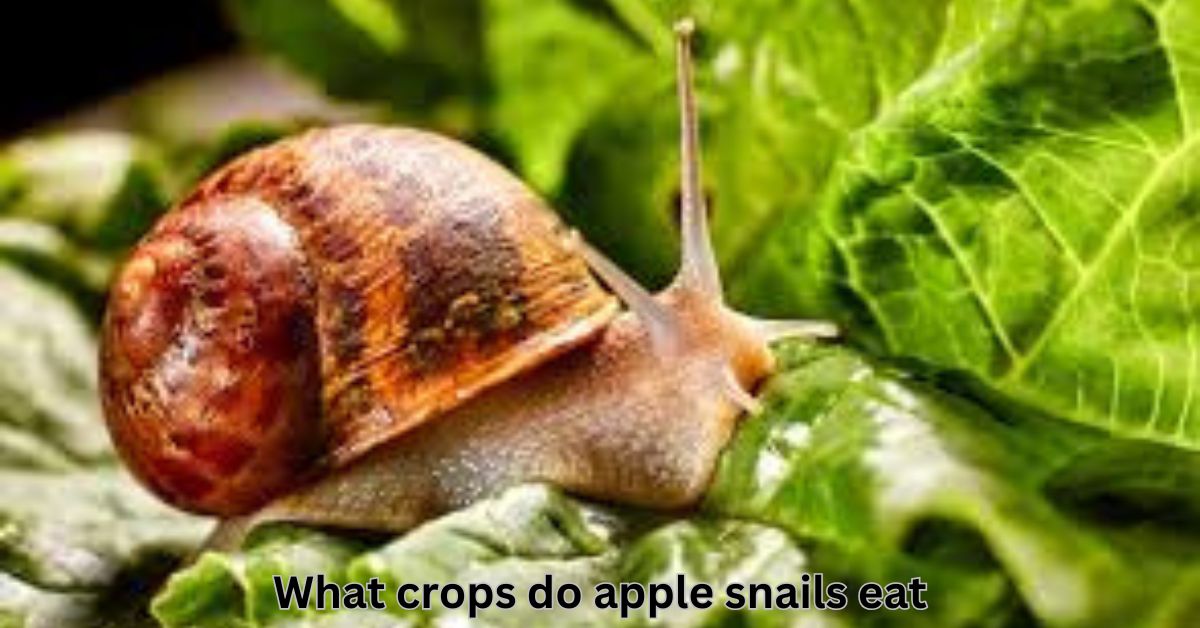

What Crops Do Apple Snails Eat? A Comprehensive Guide to Apple Snail Diet
Apple snails are fascinating creatures that can be found in freshwater environments, including lakes, ponds, and rivers. These snails are known for their ability to thrive in a variety of ecosystems and have become notorious for their impact on crops, particularly in agricultural settings. Their ability to feed on a range of plants has made them both a subject of interest and a pest in many regions. In this article, we will delve into the crops that apple snails eat, how they impact agricultural industries, and provide useful insights on managing these mollusks in farming environments.
Understanding Apple Snails
Apple snails (Pomacea canaliculata) are freshwater snails native to South America but have spread to various parts of the world, including Southeast Asia, the United States, and parts of Africa. These snails are known for their large, round shells that are often brightly colored, ranging from golden yellow to dark brown. Apple snails are omnivores, feeding on both plant material and detritus, but their main diet consists of a wide variety of aquatic plants.
While apple snails are often kept as pets in aquariums, their role as agricultural pests is a growing concern. Invasive populations of apple snails have caused significant damage to rice fields, vegetable crops, and other agricultural settings. Let’s explore the crops that apple snails tend to feed on and the impact they have on farming.
Crops That Apple Snails Commonly Eat
Apple snails are highly opportunistic feeders and have a wide range of food sources. Their diet mainly includes aquatic plants, but they can also damage crops grown in waterlogged or flooded conditions. Here are some of the primary crops and plants that apple snails consume:
1. Rice
Rice paddies are one of the most affected agricultural environments when it comes to apple snail infestations. Rice is a staple crop that requires flooded fields for cultivation, making it the perfect environment for apple snails to thrive. These snails are particularly destructive during the early stages of rice growth, where the seedlings are vulnerable to feeding.
Apple snails feed on both the tender leaves and roots of rice plants, causing them to wilt or die. This can result in significant losses for rice farmers, especially in areas where rice cultivation is a primary agricultural activity. In fact, apple snails are considered one of the most damaging pests in rice production in regions like Southeast Asia and parts of the southern United States.
2. Water Spinach (Kang Kong)
Water spinach, also known as kang kong or water morning glory, is a popular leafy vegetable in many Southeast Asian countries. It thrives in waterlogged soils or flooded environments, making it highly susceptible to damage from apple snails. The snails feed on the leaves, stems, and even the roots of the water spinach plant.
Farmers who grow water spinach often report significant damage from apple snails, as the snails can rapidly defoliate the crops, leaving little to harvest. In addition to causing direct damage to the plants, apple snails also contribute to the spread of diseases and pests by creating wounds on the plant’s surface.
3. Aquatic Plants and Water Crops
Apple snails have a preference for aquatic plants in general. Crops that are grown in wetland environments or submerged in water are particularly vulnerable to apple snail feeding. These include crops such as:
- Taro: Taro is a water-loving plant that thrives in wet soils or flooded fields. Apple snails can damage the plant by feeding on the leaves, roots, and tubers, leading to stunted growth or complete crop failure.
- Lotus: Lotus plants are often cultivated in rice paddies and ponds. Apple snails may consume the leaves and roots, leading to the plant’s demise.
- Water lilies: Although water lilies are often used for ornamental purposes in gardens and water features, they are also grown as crops in some regions. Apple snails can be quite destructive to water lilies by feeding on their leaves and stems.
4. Sugar Cane
In addition to aquatic plants, apple snails can also damage crops that grow in wet environments, such as sugar cane. Apple snails may target the young, tender shoots of sugar cane, feeding on the leaves and causing stress to the plants. The damage may reduce the yield and quality of the sugar cane crop, particularly in regions with heavy irrigation.
While sugar cane is not the primary crop targeted by apple snails, they can still cause considerable damage in areas where sugar cane is grown alongside other water-dependent crops.
5. Other Vegetables
Apple snails are also known to feed on a variety of terrestrial vegetables, especially those grown in waterlogged conditions. Some common vegetables that can be affected by apple snails include:
- Cabbage: While cabbage is primarily grown in dry soil, it can still be impacted by apple snails when irrigation systems flood the field. Apple snails are attracted to the tender leaves and may cause significant defoliation.
- Lettuce: Lettuce plants grown in wet soil or hydroponic systems are particularly susceptible to apple snail feeding. The snails can easily damage the leaves, making them unsuitable for harvest.
- Celery: Celery is another vegetable that can suffer from apple snail infestations, particularly in areas where the soil remains moist or saturated.
The Impact of Apple Snails on Agriculture
Apple snails can have a profound impact on agriculture, especially in regions where they are considered an invasive species. Their ability to rapidly reproduce and their voracious appetite make them a significant threat to various crops, particularly in flooded fields and wetland environments.
1. Crop Damage and Yield Loss
Apple snails are capable of consuming large quantities of plant material, and their feeding habits can result in severe crop damage. In rice fields, for example, a single apple snail can devour several rice seedlings in a single day. This level of feeding can significantly reduce crop yields and result in financial losses for farmers.
In addition to direct feeding damage, apple snails can also create conditions that promote the growth of fungal and bacterial diseases. By chewing on plants and creating open wounds, the snails make it easier for pathogens to infect crops.
2. Environmental Impact
Apple snails do not only affect crops but also have a broader environmental impact. As they feed on aquatic plants, they disrupt the balance of ecosystems by removing plant cover that provides food and shelter for other organisms. The loss of these plants can lead to the decline of fish populations, disrupt water filtration, and negatively impact the biodiversity of wetland habitats.
Furthermore, apple snails are known to reproduce quickly and spread rapidly across different regions. This invasive species can outcompete native snails and other aquatic organisms, leading to long-term ecological changes.
3. Control and Management Strategies
Farmers and environmental authorities have implemented various control methods to manage apple snail populations and reduce their impact on crops. Some of the most common control strategies include:
- Manual Removal: In small-scale farming operations, farmers may manually remove apple snails from their crops. While this method can be labor-intensive, it may help control local populations.
- Chemical Control: Pesticides and molluscicides can be used to target apple snails, but these chemicals can also harm other wildlife and the environment. Care must be taken when using chemical control methods to ensure that they do not have unintended consequences.
- Biological Control: Introducing natural predators of apple snails, such as certain fish species or predatory snails, can help control their population. However, this method must be carefully monitored to avoid introducing new invasive species.
- Cultural Practices: Altering farming practices, such as adjusting irrigation schedules, can help reduce the conditions that favor apple snail infestations. For instance, maintaining drier conditions in rice paddies or flooding fields at specific times may help disrupt the snails’ lifecycle.
Conclusion
Apple snails are an invasive species that pose a significant threat to a wide range of crops, particularly those grown in waterlogged or flooded environments. They feed on a variety of plants, including rice, water spinach, aquatic plants, and vegetables. Their feeding habits can cause severe crop damage, reduced yields, and environmental disruption. To manage apple snail populations, farmers and environmental authorities must employ a combination of control strategies, including manual removal, chemical control, and biological control, while considering the broader ecological impact.
By understanding what crops apple snails eat and the damage they can cause, farmers can take proactive steps to protect their crops and minimize the negative effects of these destructive mollusks.
GENERAL
Unveiling the Woman Behind Andre Hakkak wife
GENERAL
Unpacking R.A.C.E.S: What Does It Really Stand For?
GENERAL
Exploring Canvas Shapes: Unlocking Creative Possibilities

Exploring Canvas Shapes: Unlocking Creative Possibilities
When it comes to creating art, the canvas is often the first thing that artists think about. Traditionally, canvases have been rectangular or square, but today’s artists are embracing a broader variety of canvas shapes that open up new realms of creativity. Exploring canvas shapes can unlock a world of artistic possibilities, allowing artists to break free from convention and experiment with their compositions in unique and exciting ways.
In this article, we will dive into the various canvas shapes available to artists, how to use them to enhance creativity, and how these shapes influence the final artwork. Whether you’re an aspiring artist or an experienced creator, this guide will help you unlock the full potential of your artistic endeavors.
The Traditional Canvas: Rectangular and Square
Before exploring unconventional shapes, it’s important to acknowledge the classic and still widely used rectangular and square canvases. These shapes have been the staple of art for centuries and are associated with some of the most iconic works of art.
1. The Rectangle
The rectangular canvas is the most commonly used shape in traditional art. Whether in landscape or portrait orientation, rectangular canvases provide artists with a balanced area to express their ideas. The long, wide surface is perfect for creating expansive compositions, such as landscapes or cityscapes. Many Renaissance paintings and classical works feature large, rectangular canvases that allowed artists to spread out their scenes and compositions.
-
Landscape Orientation: When using a rectangular canvas in landscape orientation, artists have the freedom to depict expansive vistas, broad landscapes, and horizontal themes. The width of the canvas helps create a sense of space and movement.
-
Portrait Orientation: The portrait orientation is great for portraits, full-body depictions, or vertical compositions that emphasize height or dramatic focus. Portraits of historical figures or spiritual depictions often feature tall, narrow canvases to accentuate their vertical composition.
2. The Square
Square canvases are symmetrical and have an even balance between width and height. While less commonly used than rectangular ones, square canvases are an excellent choice for artists who want to create work that feels equal in all directions. This shape is great for more modern or experimental artwork that doesn’t necessarily rely on the classical concept of space and perspective.
Artists like Piet Mondrian and Andy Warhol utilized square canvases to create their abstract works. The square format allows for a sense of order and harmony in a composition and can often evoke a feeling of stability.
Unlocking Creativity with Non-Traditional Canvas Shapes
While rectangular and square canvases are the most widely used, non-traditional canvas shapes are gaining popularity among artists. These unique canvases encourage experimentation and innovation, pushing artists to think outside the box (literally).
1. Circular Canvases
The circle has been used in art for centuries, representing everything from the cyclical nature of life to the concept of eternity. By using a circular canvas, artists can create a work that focuses on unity and flow. Circular canvases are perfect for creating works that emphasize balance and symmetry.
Circular canvases can be particularly powerful for certain types of artworks, such as mandalas or abstract compositions. The continuous curve of the circle draws the eye inward and encourages the viewer to examine the artwork from all angles. Additionally, circular canvases are excellent for creating paintings that have a spiritual or cosmic feel.
2. Triangular Canvases
For those seeking to explore geometry and abstract concepts, triangular canvases provide a striking option. A triangle naturally suggests stability and balance, but it can also be dynamic and challenging depending on how it is oriented. Artists can play with the angles and lines of a triangular canvas to create visual tension or harmony.
Triangular canvases are often seen in modern and contemporary art, where the artist might use the shape to emphasize angles, edges, and geometric patterns. Triangular canvases can also evoke themes of direction or movement, as the sharp points of the triangle suggest forward momentum.
3. Oval Canvases
An oval canvas is an elegant choice for artists who want to create a unique composition with a sense of movement and flow. The oval shape can create a softer, more organic feel, which is ideal for figurative and nature-inspired work. Oval canvases are often used in portraiture, as the shape complements the human form and adds an element of fluidity to the composition.
Oval canvases are less common than other shapes, making them an excellent choice for artists looking to differentiate their work. They can evoke themes of transformation, natural beauty, and the passage of time, depending on the subject matter.
4. Custom-Shaped Canvases
One of the most exciting aspects of modern art is the freedom to create custom-shaped canvases. Artists can cut their own canvas into any shape they desire, allowing for complete freedom in composition and expression. This approach is commonly used in installation art and sculpture, where the canvas is treated as a three-dimensional object rather than just a flat surface.
Custom-shaped canvases can be anything from organic, flowing curves to angular, jagged edges that interact with the space around them. Artists can experiment with shapes that evoke specific feelings or ideas, and the shape itself can become an integral part of the artwork’s message.
How Canvas Shapes Influence Artistic Expression
The shape of the canvas you choose can significantly affect how you approach your artwork. Here are some ways in which the canvas shape influences creative expression:
1. Composition and Balance
Different canvas shapes require different approaches to composition. For example, a rectangular canvas often prompts an artist to think in terms of depth, space, and perspective, as it encourages horizontal or vertical lines that lead the viewer’s eye across the work. A circle or oval might lead to a more centralized or symmetrical composition, while triangular shapes could inspire an artist to explore lines, angles, and geometric abstraction.
The canvas shape can determine how an artist organizes their elements, such as the placement of focal points and the use of negative space. In many cases, the shape itself can guide the flow of the artwork, leading to a more intentional and cohesive design.
2. Movement and Emotion
The shape of the canvas can also influence the emotional tone of the piece. A square canvas may evoke feelings of stability and order, while a circle may communicate continuity or infinity. A triangle can create a sense of tension or dynamism, while a custom-shaped canvas can evoke a sense of individuality or abstraction.
In essence, the shape of the canvas becomes an active participant in the artwork, contributing to its overall meaning and emotional impact.
3. Creativity and Innovation
Exploring different canvas shapes encourages innovation. Artists who choose non-traditional shapes are forced to think creatively about how to compose and balance their work. Rather than adhering to conventional forms, artists are empowered to break the rules and experiment with the physicality of the canvas itself.
Custom shapes also allow for more interaction with the surrounding space. For example, an irregularly shaped canvas can influence how the viewer perceives the piece in a gallery setting or in the context of an installation.
Choosing the Right Canvas Shape for Your Artwork
While traditional rectangular and square canvases are tried and true, experimenting with unique shapes can bring new life to your artistic practice. Here are some considerations when selecting the best canvas shape for your work:
-
Subject Matter: Consider how the shape of the canvas will interact with your subject matter. For instance, portrait artists may find oval or circular canvases to be a natural fit, while abstract artists may enjoy the freedom of a triangular or custom-shaped canvas.
-
Message and Emotion: Think about the emotional tone you want to convey. Do you want stability, fluidity, tension, or freedom? The shape of the canvas can amplify these feelings.
-
Space: Consider the space where the artwork will be displayed. Some shapes, such as rectangular or square canvases, may be more suited for traditional gallery walls, while custom shapes or installations might interact better with open spaces.
Conclusion
Exploring canvas shapes is a journey that opens up a world of creative possibilities for artists. By breaking free from traditional formats, artists can discover new ways to express themselves, from geometric abstraction to organic, flowing compositions. Whether you choose a classic rectangular canvas or experiment with circular, triangular, or custom shapes, the right canvas can enhance your creative expression and help you achieve your artistic vision. Embrace the possibilities that different canvas shapes provide, and let your creativity guide the way.
-

 TECHNOLOGY2 months ago
TECHNOLOGY2 months agoWhat happened to spank bang
-
 ENTERTAINMENT2 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT2 months agoWhat Is JerkMate? Exploring the Features and Purpose
-

 FASHION2 months ago
FASHION2 months agoUnderstanding the Carmelita Neck: A Unique Fashion Detail
-

 GENERAL2 months ago
GENERAL2 months agoUnveiling the 322 Messianic Prophecies: A Deep Dive
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoDebonair blog:The Art of Stylish Living
-

 BUSNIESS2 months ago
BUSNIESS2 months agoCrypto FintechZoom: Navigating the Future of Digital Finance
-

 ENTERTAINMENT2 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT2 months agoWhat Does It Mean to Be a Scratch Golfer?
-

 BUSNIESS2 months ago
BUSNIESS2 months agoTNA Board: Shaping the Future of Innovation and Leadership


