HEALTH
Essential Items in a First Aid Kit for Snake Bites
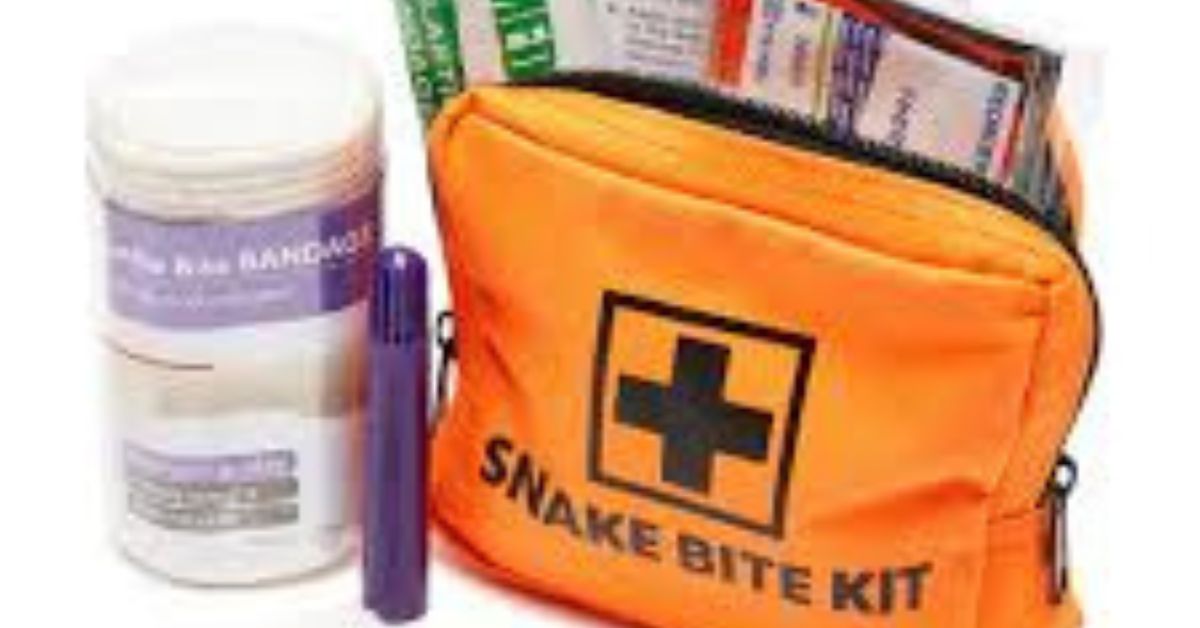
HEALTH
Lubed: Smooth Moves, Bold Confidence

Lubed: Smooth Moves, Bold Confidence
In today’s modern world, confidence and comfort go hand-in-hand—especially when it comes to intimacy and personal wellness. Lubed is more than just a personal lubricant; it’s a lifestyle enhancer that champions self-expression, connection, and ultimate ease. Whether you’re navigating intimate moments or simply want to feel more in tune with your body, Lubed provides the glide and assurance you need to move through life smoothly.
🔍 What is Lubed?
Lubed is a premium personal lubricant brand designed for people who prioritize both comfort and quality. It’s formulated to enhance intimate experiences while promoting body positivity and sexual confidence. Unlike many lubricants that feel sticky or artificial, Lubed’s focuses on natural-feel formulas that mimic the body’s own moisture, making each experience seamless and satisfying.
Available in various types—from water-based and silicone blends to organic and flavored options—Lubed caters to a broad range of preferences and needs.
🌿 Ingredients That Care for You
✅ Skin-Friendly Formulas
One of the standout features of Lubed is its commitment to skin-friendly ingredients. Whether you’re sensitive to certain additives or prefer a product that’s clean and simple, Lubed has you covered.
-
Water-based options: Safe with condoms and sex toys, easy to clean, and gentle on all skin types.
-
Silicone-based lubes: Perfect for longer-lasting sessions, especially under water.
-
Organic and natural formulas: Free from parabens, glycerin, and artificial fragrances.
🧪 Dermatologist-Tested
All Lubed’s products are rigorously tested for safety and performance. Dermatologist-approved and hypoallergenic, they offer peace of mind alongside pleasure.
💧 Why Use Lubed?
1. Enhanced Intimacy
Whether you’re with a partner or enjoying solo time, lubrication significantly enhances physical comfort and sensation. Lubed reduces friction, preventing irritation and making intimate experiences more enjoyable and natural.
2. Supports Confidence and Connection
Dryness can cause discomfort, insecurity, or distraction. Lubed empowers you to stay present, confident, and connected—whether you’re exploring new boundaries or just trying to feel more like yourself.
3. Inclusive Pleasure
Lubed is designed with all bodies, orientations, and identities in mind. The brand encourages open conversations around sexuality, breaking down taboos while promoting safe, consensual fun.
🌈 Types of Lubed Products
💦 Water-Based Lubricants
Perfect for beginners and everyday use, water-based Lubed’s options are compatible with all condoms and toys. They’re easy to wash off and won’t stain sheets or clothing.
Best for: Vaginal sex, toy play, quick cleanup.
🌊 Silicone-Based Lubricants
Silicone lubes provide longer-lasting glide without the need for frequent reapplication. They’re especially great for water play and endurance activities.
Best for: Shower or bath intimacy, anal sex, extended sessions.
🌱 Organic Lubricants
Formulated from plant-based ingredients, these are ideal for those with sensitive skin or eco-conscious consumers who prefer clean products.
Best for: Sensitive users, wellness-focused lifestyles, green-conscious shoppers.
🍓 Flavored Lubes
Lubed offers fun and delicious options in a variety of flavors, from vanilla bean to wild strawberry. Perfect for oral exploration and adding a little excitement to your intimacy.
Best for: Oral sex, playful experiences, sensual variety.
🔥 Lubed in Real Life: Smooth Moves Beyond the Bedroom
While traditionally used in intimate settings, Lubed’s can also enhance comfort in everyday scenarios. Here are a few surprising ways people use Lubed:
-
Chafing prevention during workouts
-
Post-shaving skin soothing
-
Latex garment dressing aid
-
Massage lubricant alternative
The versatility of Lubed’s makes it more than a one-use product—it becomes an essential in any self-care routine.
🛡️ Is Lubed Safe to Use?
Absolutely. Lubed’s is formulated with safety and body compatibility in mind. Here’s why it’s trusted by many:
-
Condom-safe: Especially the water-based and silicone formulas.
-
Gynecologist-recommended: Many professionals approve of Lubed for reducing dryness without disrupting vaginal flora.
-
Non-toxic and cruelty-free: Ethical testing and clean sourcing are top priorities.
However, it’s always recommended to do a patch test and consult a healthcare provider if you have specific allergies or skin sensitivities.
🛍️ Where to Buy Lubed’s
You can find Lubed products at:
-
Online: Through the official Lubed website or major retailers like Amazon, Walmart, and drugstores.
-
In-store: Most adult stores, pharmacies, and wellness retailers carry the Lubed range.
Look for special edition kits, travel sizes, and subscription options if you want to keep your bedside drawer stocked.
📣 Real Reviews, Real Confidence
Here’s what people are saying about Lubed:
“Lubed changed the game for me. It’s smooth, natural, and feels like an extension of my body.” – Jenna T.
“The silicone lube is my go-to. Works in the shower and doesn’t quit!” – Marcus D.
“Finally found a lube that doesn’t irritate me. The organic one is my absolute favorite.” – Taylor M.
💡 Final Thoughts: Why Lubed is the Confidence Boost You Didn’t Know You Needed
Lubed’s is more than a lubricant—it’s a gateway to bold, unfiltered confidence. Whether you’re enhancing intimacy, exploring your body, or simply avoiding discomfort, Lubed’s ensures you’re always ready to glide into the moment.
By offering safe, inclusive, and versatile solutions, Lubed’s truly delivers on its promise: Smooth Moves. Bold Confidence.
HEALTH
Muscle and Joint Chiropractic: Pain Relief and Mobility
HEALTH
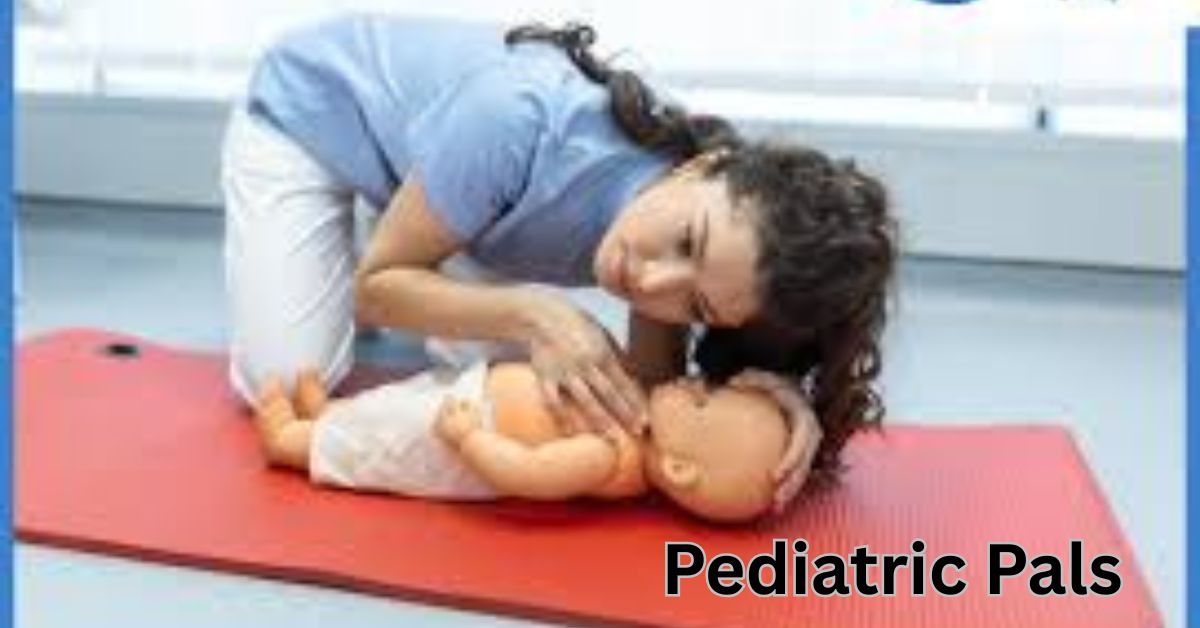
Compassionate Care: The Power of Pediatric PALS
-

 TECHNOLOGY3 months ago
TECHNOLOGY3 months agoWhat happened to spank bang
-
 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Is JerkMate? Exploring the Features and Purpose
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoUnderstanding the Carmelita Neck: A Unique Fashion Detail
-

 GENERAL3 months ago
GENERAL3 months agoUnveiling the 322 Messianic Prophecies: A Deep Dive
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoDebonair blog:The Art of Stylish Living
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoDrake Exposed: The Untold Truth Behind the Music and Fame
-

 BUSNIESS3 months ago
BUSNIESS3 months agoCrypto FintechZoom: Navigating the Future of Digital Finance
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Does It Mean to Be a Scratch Golfer?


