GENERAL
Understanding Pigeon Diets: What Do Pigeons Eat?

GENERAL
Top Stays in Osaka: Where Comfort Meets Convenience
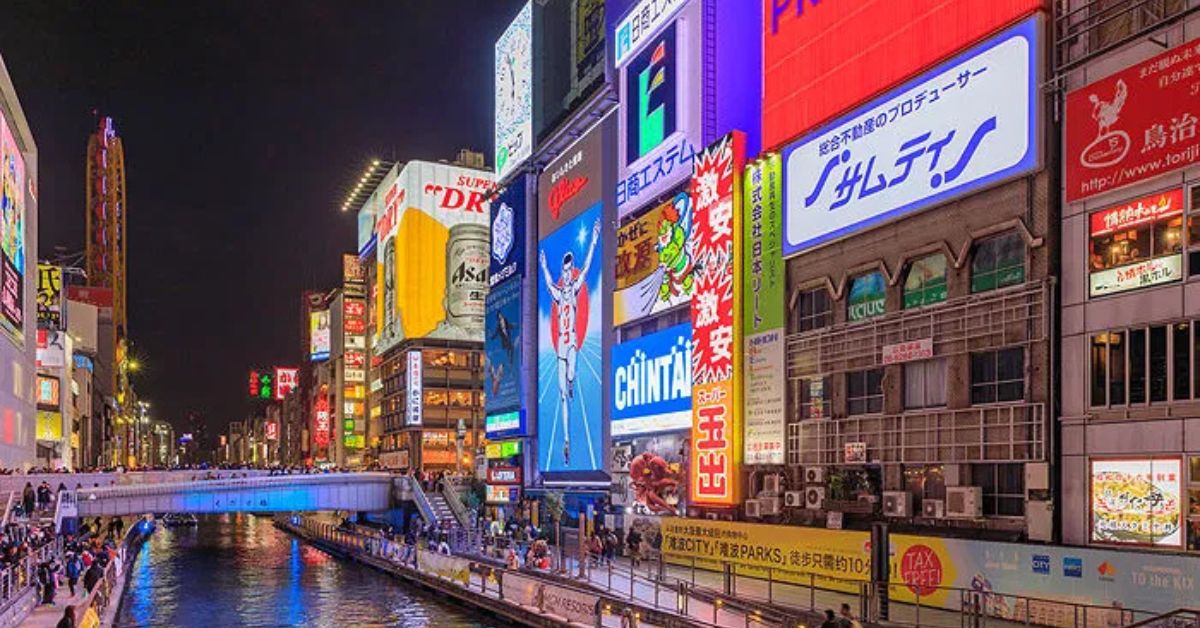

Top Stays in Osaka: Where Comfort Meets Convenience
Osaka, one of Japan’s most dynamic cities, is a destination that blends tradition with modernity, creating a unique environment for tourists. Whether you’re visiting for business, leisure, or a little bit of both, finding the right place to stay is crucial to making the most of your trip. In this article, we explore the best places to stay in Osaka, where comfort meets convenience. From luxurious hotels to cozy boutique stays, we’ve got a selection of the top accommodations that cater to all tastes and budgets.
Why Osaka?
Before diving into the best stays, let’s take a moment to understand why Osaka is such a fantastic destination. Known for its vibrant street food scene, historical landmarks, and cutting-edge shopping districts, Osaka is a city that never sleeps. Whether you’re exploring the bustling streets of Dotonbori, taking in the scenic views from Osaka Castle, or shopping in Shinsaibashi, there’s always something to do.
With so much to see and experience, staying in the right location can make a big difference in your Osaka trip. From the excitement of Namba to the cultural heart of Umeda, the right stay can provide the perfect home base for exploring the city.
Best Areas to Stay in Osaka
1. Namba: The Heart of Osaka’s Entertainment District
For travelers who want to immerse themselves in the energy of Osaka, Namba is the place to be. Located in the southern part of Osaka, Namba is the city’s entertainment epicenter. The area is home to Dotonbori, a famous street filled with neon lights, eateries, and shops, making it a lively and exciting neighborhood for visitors.
Namba is well-connected by public transport, including Namba Station, which is one of Osaka’s major transit hubs. Staying here puts you right in the middle of the action, with easy access to entertainment, dining, and shopping.
Best for: First-time visitors, food lovers, nightlife enthusiasts.
2. Umeda: Osaka’s Commercial Hub
For those seeking a more business-focused trip or a quiet yet convenient area with modern amenities, Umeda is the best option. Known as Osaka’s commercial center, Umeda features iconic buildings such as the Umeda Sky Building and the Grand Front Osaka complex, which hosts upscale shopping, dining, and entertainment options.
Umeda is also home to several luxury hotels and department stores, making it an ideal place to stay if you’re looking for comfort with easy access to other parts of the city. It’s also well-connected by the Osaka Station, a major transportation hub that can easily take you to Kyoto, Nara, or Kobe.
Best for: Business travelers, luxury seekers, shoppers.
3. Shin-Osaka: Perfect for Convenient Transportation
If you’re planning to explore other regions of Japan or just need quick access to the Shinkansen, Shin-Osaka is a great area to stay. Situated around Shin-Osaka Station, it offers a more relaxed atmosphere compared to the bustling Namba and Umeda. It’s ideal for travelers who prioritize convenience and transportation access, especially those visiting multiple cities or traveling on the high-speed bullet train.
While Shin-Osaka is quieter and less crowded, it still offers a good selection of accommodations, from budget options to mid-range hotels.
Best for: Transit-focused travelers, those visiting multiple cities, families.
4. Shinsaibashi: Shopping, Dining, and Culture
Another bustling district in Osaka is Shinsaibashi, famous for its shopping arcades and proximity to the lively Dotonbori area. Shinsaibashi is where you’ll find luxury boutiques, trendy fashion outlets, and eclectic local shops. The area is known for its rich blend of traditional Japanese culture and modern flair, making it a fantastic place to shop, eat, and explore.
If you love shopping and the vibrant atmosphere of city life, Shinsaibashi offers a blend of both worlds. The Shinsaibashi Shopping Arcade is a must-visit for those looking to bring back unique souvenirs or fashion finds.
Best for: Shopping enthusiasts, culture lovers, foodies.
Top Stays in Osaka
Now that we’ve covered some of the best areas in Osaka, let’s dive into the top stays that blend comfort with convenience. Whether you’re looking for luxury or budget-friendly options, these accommodations will ensure a memorable stay in Osaka.
1. The St. Regis Osaka
If you’re looking for luxury in the heart of Osaka, The St. Regis Osaka is one of the best choices. Located in the Umeda district, this five-star hotel offers sophisticated accommodations, impeccable service, and world-class dining. The St. Regis Osaka blends modern elegance with traditional Japanese design, offering guests an exceptional experience.
Key features:
-
Luxurious rooms with modern amenities
-
A Michelin-starred restaurant, La Veduta
-
Stunning city views from the rooms
-
Spa and wellness center for relaxation
Best for: Luxury travelers, honeymooners, business trips.
2. Swissôtel Nankai Osaka
Situated directly above Namba Station, Swissôtel Nankai Osaka offers guests a prime location right in the center of Osaka’s vibrant entertainment district. With easy access to shopping, dining, and transportation, this hotel is a top pick for travelers who want to be near the action.
Key features:
-
Stylish and spacious rooms with panoramic views of the city
-
Multiple dining options, including an all-day buffet and Japanese cuisine
-
Fitness center, spa, and outdoor pool
Best for: Travelers seeking a luxurious yet central stay, families.
3. Hotel Universal Port
For families and theme park lovers, Hotel Universal Port is a perfect choice. Located near Universal Studios Japan, this hotel offers a fun and convenient base for those visiting the popular theme park. The rooms are themed around movie characters, making it especially enjoyable for kids.
Key features:
-
Family-friendly rooms with themed decor
-
Free shuttle service to Universal Studios Japan
-
A variety of dining options, including kid-friendly menus
Best for: Families, Universal Studios Japan visitors, fun seekers.
4. The Park Front Hotel at Universal Studios Japan
Another fantastic option for those visiting Universal Studios Japan is The Park Front Hotel. Located near the park entrance, it offers easy access to the rides, shows, and attractions. It’s also equipped with modern amenities and stylish interiors, making it an ideal place to relax after a busy day at the park.
Key features:
-
Proximity to Universal Studios Japan
-
Contemporary rooms with city or park views
-
Dining options and a cafe with a modern atmosphere
Best for: Universal Studios Japan visitors, short stays.
5. Hotel Nikko Osaka
For travelers who want a combination of convenience and comfort, Hotel Nikko Osaka is an excellent choice. Located near the Shinsaibashi and Namba districts, the hotel provides easy access to shopping, dining, and entertainment. The rooms are comfortable and well-equipped, ensuring a pleasant stay for both short and long visits.
Key features:
-
Located near the Shinsaibashi Shopping Arcade
-
Free Wi-Fi and modern room amenities
-
Multiple dining options, including Japanese and Western cuisine
Best for: Shopping enthusiasts, cultural explorers, and mid-range travelers.
6. Capsule Hotel Anshin Oyado Premier
For those on a budget or seeking a unique experience, Capsule Hotel Anshin Oyado Premier offers a modern take on traditional capsule hotels. Located in the Namba area, this capsule hotel provides guests with compact yet comfortable sleeping pods. It’s a fantastic option for solo travelers looking for affordable, efficient, and clean accommodations.
Key features:
-
Private capsule rooms with a TV, Wi-Fi, and air conditioning
-
Sauna and relaxation areas
-
Affordable and convenient
Best for: Solo travelers, budget-conscious guests, those seeking a unique stay.
Conclusion: Where Comfort Meets Convenience in Osaka
Osaka is a vibrant and diverse city that offers something for every type of traveler. Whether you’re staying in the heart of Namba, the business-centric Umeda, or the quiet yet accessible Shin-Osaka, the city offers a range of accommodations that provide both comfort and convenience.
From luxury hotels like The St. Regis Osaka to family-friendly options like Hotel Universal Port, there’s no shortage of places to rest your head while exploring this amazing city. With the right stay, your trip to Osaka can be filled with unforgettable experiences, relaxation, and adventure.
So, whether you’re visiting for the first time or returning for more exploration, choosing the right place to stay will ensure you make the most of your time in Osaka. Remember, your accommodation should be as memorable as the sights and sounds of the city itself.
GENERAL
Charlie Tan: A Name to Remember

Charlie Tan: A Name to Remember
In a world brimming with remarkable individuals making waves in various fields, Charlie Tan stands out as a name that continues to capture attention for his multifaceted achievements. From his contributions to industry innovations to his personal journey of success, Charlie Tan is not just a name but a brand symbolizing excellence, determination, and ingenuity. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of Charlie Tan’s life, career, and impact that have cemented his reputation as a name to remember.
Who is Charlie Tan?
A Multifaceted Talent
Charlie Tan is a name that resonates with innovation, leadership, and success. While many might not know him at first glance, his contributions across multiple sectors, from business to technology and even social causes, have left a lasting mark. His name represents someone who has broken barriers and demonstrated an ability to adapt to and thrive in ever-changing environments.
Charlie Tan’s journey has been marked by a commitment to learning and improvement, both in his professional pursuits and personal endeavors. His diverse skill set and passion for progress make him a standout figure who has earned respect in the industries he has touched.
The Early Years of Charlie Tan
Humble Beginnings
Like many successful individuals, Charlie Tan’s journey to recognition began with humble roots. Raised in an environment that emphasized the importance of education and hard work, he cultivated a deep passion for learning at an early age. His curiosity and drive to understand how things work laid the foundation for his future accomplishments.
Although his upbringing wasn’t particularly glamorous, Charlie Tan’s parents instilled values of perseverance and resilience that would become crucial to his success. These early lessons, along with his academic and extracurricular achievements, would propel him toward a career that would soon make waves.
Education and Formative Experiences
Charlie Tan’s educational path was one of consistent growth. Whether it was his pursuit of specialized knowledge in technology or his involvement in community initiatives, his academic journey was not just about grades but about gaining experience that would shape his future. Charlie’s ability to understand the intersection between innovation, leadership, and human needs became evident during his time in school, where he actively participated in activities that honed his leadership abilities.
Charlie Tan’s Career: From Vision to Reality
Entering the Professional World
Upon completing his education, Charlie Tan entered the professional world with a clear vision—he wanted to make an impact. It was his blend of creativity, technical expertise, and business acumen that set him apart from his peers. Charlie’s ability to identify emerging trends and act on them helped him navigate through the competitive world, whether it was in technology, business, or other ventures.
Starting out in the tech industry, Charlie made a name for himself with his innovative approaches to problem-solving. He focused on delivering solutions that not only met the needs of customers but also anticipated future demands. His forward-thinking mindset allowed him to play a pivotal role in the companies he worked with, earning him recognition and respect.
Business and Entrepreneurship: A New Era of Innovation
As an entrepreneur, Charlie Tan took a bold step toward establishing his own ventures. His entrepreneurial spirit pushed him to create businesses that were not just about profits but about creating real value for the community. He sought to innovate by integrating technology with user-friendly solutions, which made his businesses stand out in highly competitive industries.
One of Charlie’s notable achievements is his ability to identify market gaps and fill them with practical, sustainable, and scalable solutions. This unique skill has helped him build businesses that continue to thrive today. His focus on customer-centricity, combined with cutting-edge technology, has ensured that his ventures stay relevant in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Leadership and Influence of Charlie Tan
A Natural Leader
Charlie Tan is often described as a visionary leader who possesses the unique ability to inspire those around him. His leadership style is characterized by empathy, clear communication, and an unwavering commitment to his team. He believes that leadership is not just about giving orders but about empowering others to take ownership of their roles and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
His leadership qualities have helped him cultivate strong, cohesive teams that consistently perform at the highest levels. Whether leading a startup or guiding an established business, Charlie has a knack for bringing out the best in people and fostering an environment where innovation can thrive.
Impact on Industry and Society
Charlie’s influence extends beyond just business and technology. As someone who deeply cares about societal progress, he has consistently leveraged his success to create positive change. Through philanthropy and involvement in social causes, Charlie has used his platform to advocate for issues such as education, sustainability, and equal opportunity.
His commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR) is reflected in his approach to business, where he has always strived to build ventures that have a positive impact on the communities they serve. Whether it’s through environmental initiatives, supporting local education systems, or providing mentorship to young entrepreneurs, Charlie Tan’s work extends far beyond profit-making.
Charlie Tan’s Legacy: A Name for the Future
A Visionary’s Blueprint
The legacy of Charlie Tan is not one confined to the past; it is a blueprint for the future. His vision for innovation and leadership has set a high standard for future generations. He has proven that success is not just about achieving personal milestones, but about creating a lasting, positive impact on the world.
In the years to come, Charlie’s influence will undoubtedly continue to inspire new leaders and entrepreneurs. His ability to think beyond the conventional, his resilience in the face of adversity, and his focus on creating long-term value make him a role model for anyone looking to make their mark on the world.
Mentorship and Teaching the Next Generation
As an advocate for education and personal growth, Charlie Tan has actively contributed to the development of future leaders. He has taken on mentoring roles, sharing his knowledge and experience with aspiring entrepreneurs and business leaders. This commitment to mentorship has allowed him to pass on his wisdom to the next generation, ensuring that his principles of innovation, leadership, and social responsibility continue to thrive.
His efforts in mentorship have had a ripple effect, influencing countless individuals who have gone on to create their own successful ventures or contribute meaningfully to their respective fields. Through these contributions, Charlie Tan has built an enduring legacy that goes beyond just business success.
The Future of Charlie Tan: Continuing to Inspire
An Ever-Evolving Journey
Even though Charlie Tan has already achieved so much, his journey is far from over. He continues to innovate, learn, and grow, ensuring that he remains at the forefront of change. As the world changes, so does his approach to business, leadership, and philanthropy. His continued pursuit of knowledge and excellence guarantees that his influence will only grow in the years to come.
Charlie Tan is committed to making an impact in new and exciting ways, and his adaptability ensures that he will continue to thrive in an ever-evolving world. Whether through new business ventures, community engagement, or mentorship, Charlie will undoubtedly remain a name to remember for many years to come.
Conclusion: Why Charlie Tan Is a Name to Remember
Charlie Tan’s journey is one of inspiration, resilience, and dedication. From humble beginnings to becoming a leader in his field, he exemplifies the power of perseverance and vision. His legacy is not only defined by his personal achievements but also by his ability to inspire others, create positive change, and leave an indelible mark on industries and communities alike.
In a world full of remarkable individuals, Charlie Tan stands as a beacon of innovation and leadership, proving that a name can indeed become synonymous with success, impact, and lasting influence.
GENERAL
Unveiling the Woman Behind Andre Hakkak wife
-

 TECHNOLOGY3 months ago
TECHNOLOGY3 months agoWhat happened to spank bang
-
 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Is JerkMate? Exploring the Features and Purpose
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoUnderstanding the Carmelita Neck: A Unique Fashion Detail
-

 GENERAL3 months ago
GENERAL3 months agoUnveiling the 322 Messianic Prophecies: A Deep Dive
-

 FASHION3 months ago
FASHION3 months agoDebonair blog:The Art of Stylish Living
-

 BUSNIESS3 months ago
BUSNIESS3 months agoCrypto FintechZoom: Navigating the Future of Digital Finance
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoDrake Exposed: The Untold Truth Behind the Music and Fame
-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoWhat Does It Mean to Be a Scratch Golfer?

